Your Trusted Dermatology Clinic
Pigmentary Disorders Treatment
Pigmentation means discolouration of the skin. There may be increased pigmentation like Melasma, solar melanosis, freckles, Drug induced pigmentation etc. or decreased pigmentation healing lesions, pityriasis alba, leprosy etc. or complete absence of pigment (Vitiligo)
Common Pigmentary disorders
Melasma: hormone related, dark, mottled pigmentation on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. More common after pregnancy and in women on contraceptive pills and certain other drugs. Can also be seen in men
Birthmarks: Naevus of ota, beckers naevus, congenital melanocytic naevi, junctional naevi, compound naevi etc. Commonly known as moles or birthmarks and are present since childhood.
Solar melanosis: Pigmentation on areas exposed to sunlight
Freckles: spots of pigmentation on cheeks and face due to sun damage. Runs in families and more common in fair-skinned people.
Diseases associated with pigmentation
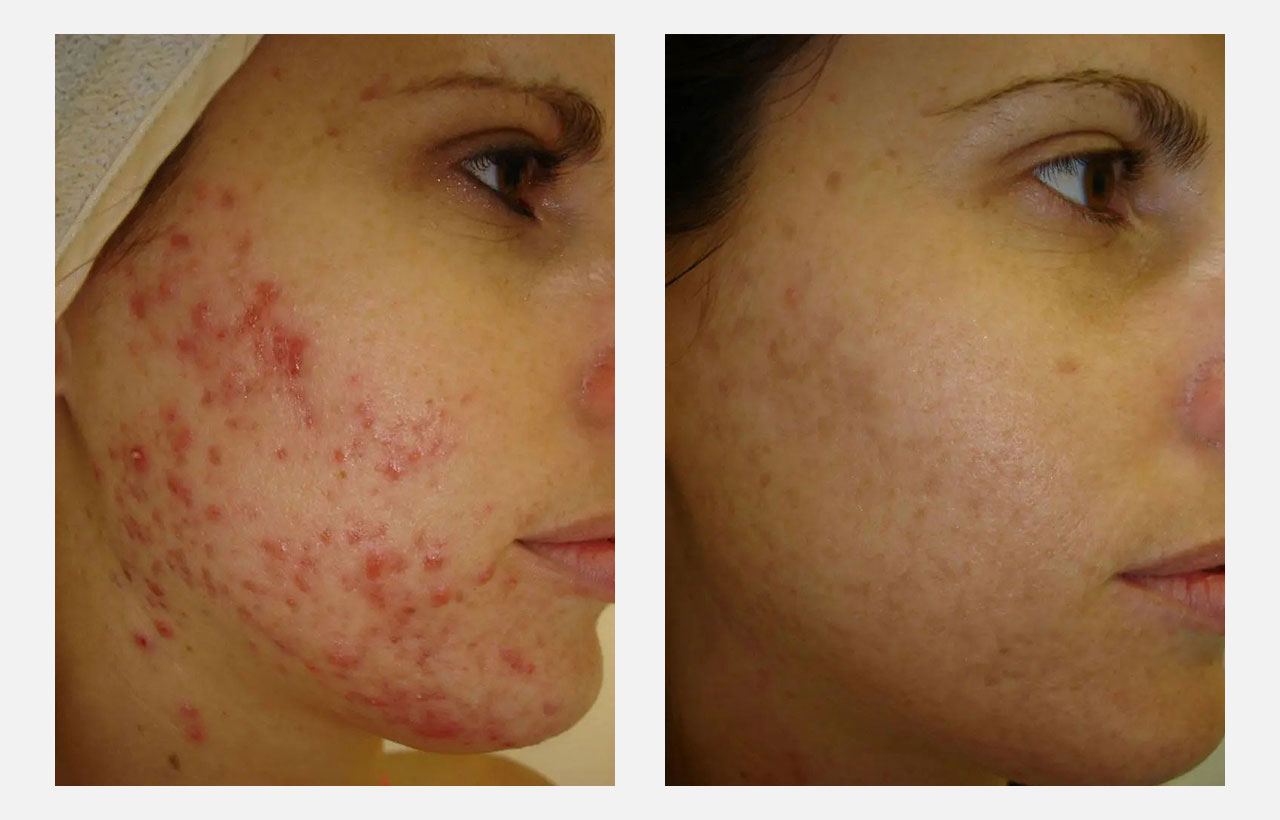
Post inflammatory pigmentation: pigmentation seen after an active skin disease is resolving, ex: after acne(pimples), seborrheic dermatitis, skin infections, psoriasis etc.
Lichen planus pigmentosus: Bluish gray pigmentation on the sun exposed areas with deep level of pigmentation
Acanthosis nigricans: due to thickening of the skin, over nape of the neck, sides of the forehead, axilla and groin,usually associated with weight gain and insulin resistance states.
About Atopic
They can also have associated asthma and allergic rhinitis (known as the atopic triad). Itchy red lesions sometimes with oozing form the hallmark of the disease. Severe itching, recurrence of patches, dry skin and a family history of similar disease is usually present. The skin in atopic children is dry and overly sensitive to a variety of environmental allergens that normal children do not react to. Most children with AD get better by 5 years of age, few of them suffer from it till the age of 12 and a very few of them continue to have it in adulthood.
Treatment is aimed at restoring the skin barrier by adequate use of emollients, controlling the acute flares and modulating the immune response by use of topical and oral medications.